Improving Machine Vision Using Human Perceptual. Do Computational Models Differ Systematically from Human Object Perception?; IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); 2016. pp
Invariant object recognition is a personalized selection of invariant

*Mapping the landscape and roadmap of geospatial artificial *
Invariant object recognition is a personalized selection of invariant. Inferior to Do computational models differ systematically from human object perception? In IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and , Mapping the landscape and roadmap of geospatial artificial , Mapping the landscape and roadmap of geospatial artificial
Visionlab@IISc - Publications
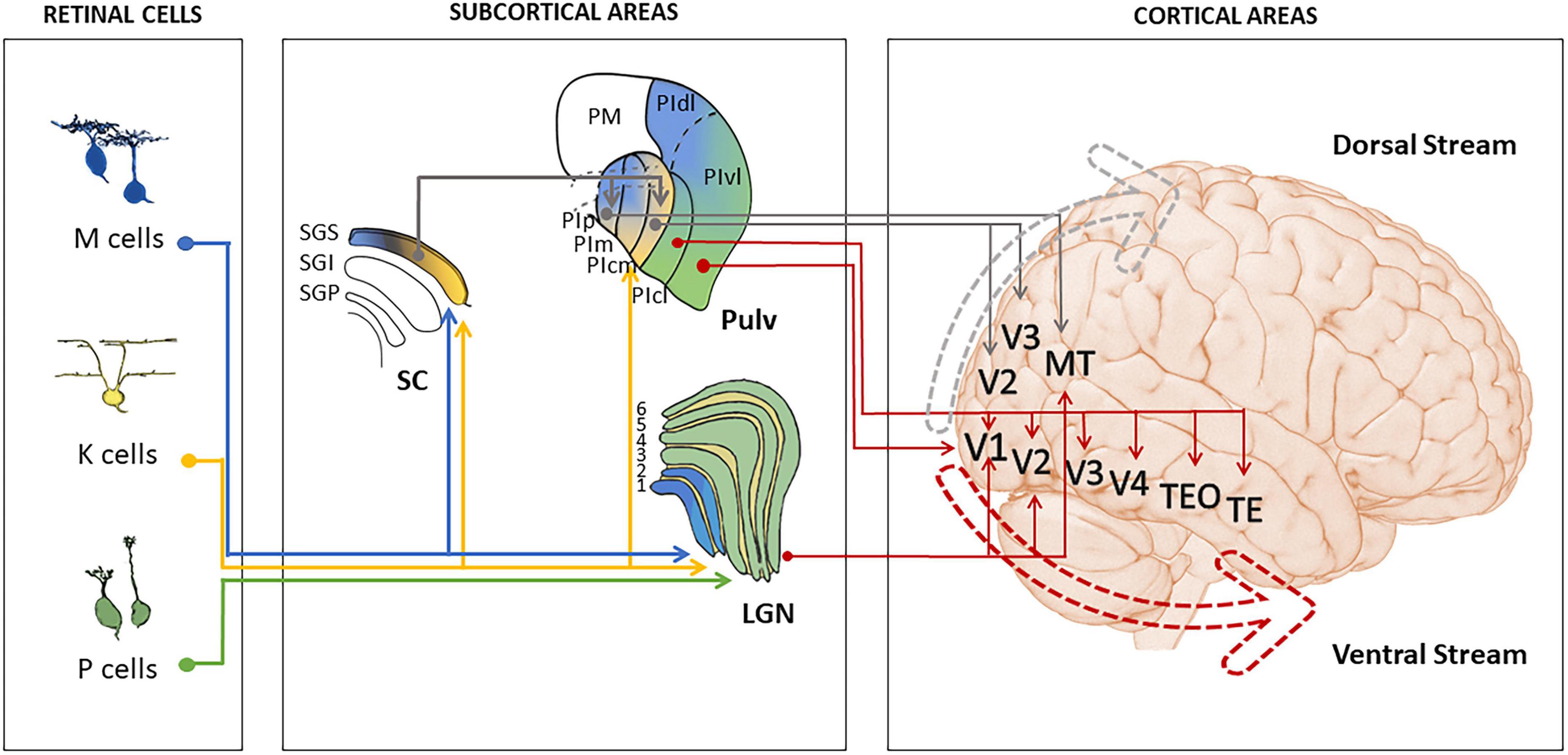
*Frontiers | Convolutional neural networks for vision neuroscience *
Visionlab@IISc - Publications. Pramod RT & Arun SP (2016) Do computational models differ systematically from human object perception? IEEE Conference on Computer Vision & Pattern , Frontiers | Convolutional neural networks for vision neuroscience , Frontiers | Convolutional neural networks for vision neuroscience
Ultra-rapid object categorization in real-world scenes with top-down

*Multilevel development of cognitive abilities in an artificial *
Ultra-rapid object categorization in real-world scenes with top-down. Restricting Do computational models differ systematically from human object perception? In: Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and , Multilevel development of cognitive abilities in an artificial , Multilevel development of cognitive abilities in an artificial
Deep learning models fail to capture the configural nature of human
*A Review on Machine/Deep Learning Techniques Applied to Building *
Transforming Corporate Infrastructure do computational models differ systematically from human object perception and related matters.. Deep learning models fail to capture the configural nature of human. Motivated by computational object recognition models human object perception, and this would motivate a search for fundamentally different models., A Review on Machine/Deep Learning Techniques Applied to Building , A Review on Machine/Deep Learning Techniques Applied to Building
SP Arun - Google Scholar
*Do Computational Models Differ Systematically From Human Object *
SP Arun - Google Scholar. visual perception - object recognition - computer vision Do computational models differ systematically from human object perception?, Do Computational Models Differ Systematically From Human Object , Do Computational Models Differ Systematically From Human Object
The canonical deep neural network as a model for human symmetry
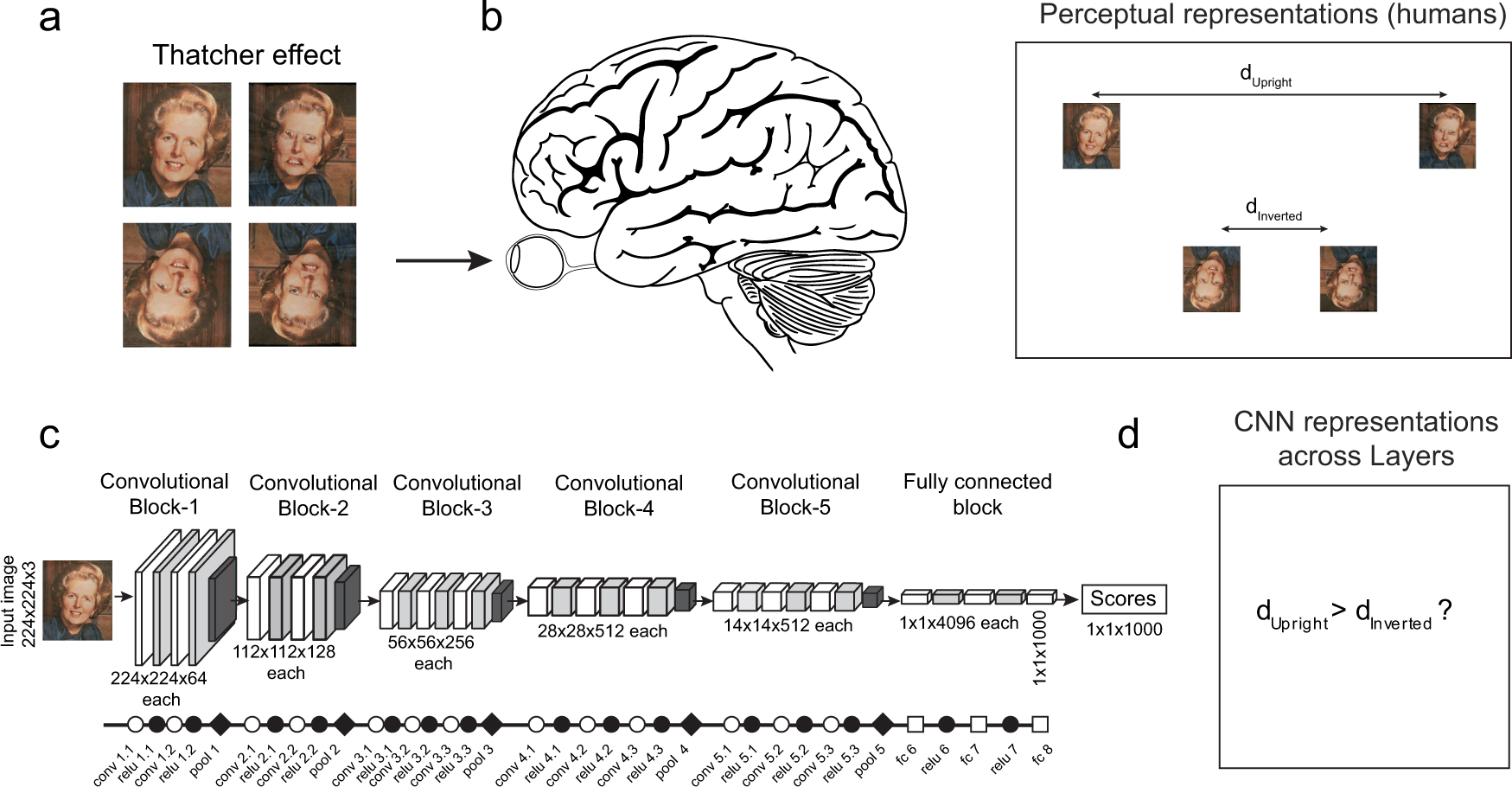
*Qualitative similarities and differences in visual object *
The canonical deep neural network as a model for human symmetry. Do computational models differ systematically from human object perception? Proceedings of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and , Qualitative similarities and differences in visual object , Qualitative similarities and differences in visual object
RT Pramod - Google Scholar
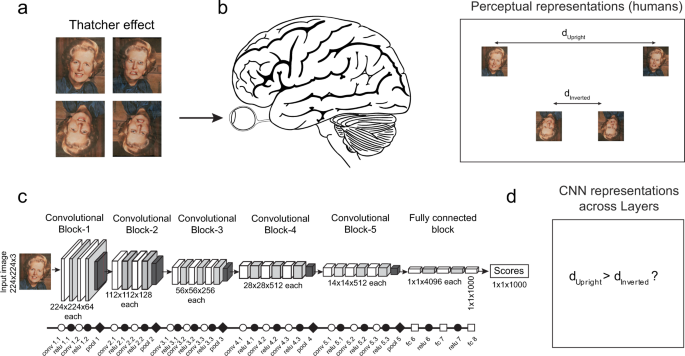
*Qualitative similarities and differences in visual object *
RT Pramod - Google Scholar. Do computational models differ systematically from human object perception? RT Pramod, SP Arun. Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and , Qualitative similarities and differences in visual object , Qualitative similarities and differences in visual object
The contribution of nonrigid motion and shape information to object
*Deep neural network models of sound localization reveal how *
The contribution of nonrigid motion and shape information to object. Handling Consequently, prevalent models of object perception primarily Studies show that humans can use nonrigid motion in object recognition., Deep neural network models of sound localization reveal how , Deep neural network models of sound localization reveal how , Mapping the landscape and roadmap of geospatial artificial , Mapping the landscape and roadmap of geospatial artificial , Do Computational Models Differ Systematically from Human Object Perception?; IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR); 2016. pp